

Higher and foundation tiers- Foundation tier students are NOT required to write ion-electron half equations for reactions happening at the electrodes. You only need to be able to predict what will be produced at the anode and cathode. You should have a good knowledge of how electrolysis works before reading this page.
 One of the main uses of electrolysis is electroplating objects.
Electroplated objects are metal objects which
are given a thin layer of another metal as an additional coating. Objects are usually
electroplated to make them more
attractive looking or to help them resist corrosion. Car, motorcycle and bike parts such as mirrors, engine parts, exhausts, and bumpers for example are often
electroplated with chromium metal to make them look attractive and also to resist corrosion.
One of the main uses of electrolysis is electroplating objects.
Electroplated objects are metal objects which
are given a thin layer of another metal as an additional coating. Objects are usually
electroplated to make them more
attractive looking or to help them resist corrosion. Car, motorcycle and bike parts such as mirrors, engine parts, exhausts, and bumpers for example are often
electroplated with chromium metal to make them look attractive and also to resist corrosion.
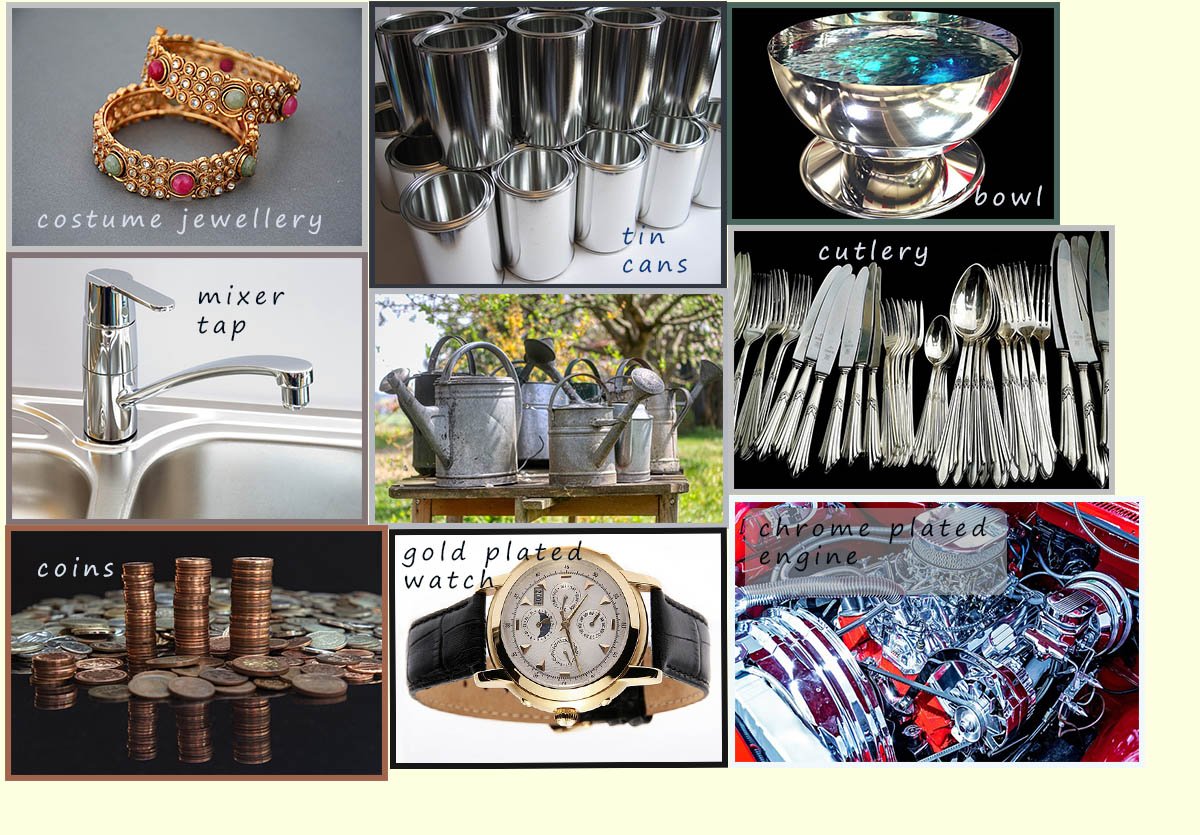
Another common use of electroplating is in the manufacture of costume jewellery, here an inexpensive metal or alloy such as brass is silver or gold plated. The reason that costume jewellery can be sold so cheaply is that the amount of silver or gold that is electroplated onto the less expensive metal is very very small. Rings, bracelets, necklaces and watches are often electroplated this way.

Copper is often used to make wires as electrical connectors for devices such as televisions, Xboxs and sound equipment such as electrical guitars, hi-fis and other musical instruments, but in time it will tarnish and its electrical conductivity will fall. Hi-end electrical connectors are gold plated. Gold is an excellent electrical conductor and being very unreactive will not tarnish, however it is far more expensive than copper or even silver which is sometimes used in connectors. However despite the extra cost associated with gold and silver plated connectors they are readily available especially on many big branded products were people are prepared to pay the extra costs for these items.
Another common example of electroplated objects are coins. Coins are often made of steel which is copper or zinc plated. Steel is a strong durable alloy but it will corrode, however copper is an unreactive metal and it will prevent the steel from corroding. Steel is much less expensive than copper; so for example if 2 pence coins were made of pure copper you could make a lot of money by simply melting them down and selling the copper metal produced! The image below shows some everyday electroplated objects and a quick search on Google will reveal many more everyday items which are electroplated.


Electroplating is very simple to carry out. The object to be plated is made the cathode in a cell, such as the one shown opposite.
The object to be electroplated must be an electrical conductor. In the example shown in the diagram a metal key is placed in a copper sulfate
solution. The copper sulfate solution contains copper ions (Cu2+(aq)) and sulfate ions (SO42-(aq)) ions.
Now once the cell starts an electrical current will flow and the metal key will become copper plated, the positively charged copper ions present in the copper sulfate solution will be attracted to the negatively charged cathode, which in this case is the metal key and once the copper ions (Cu2+(aq)) arrive at the cathode they will be reduced to form copper metal; which will plate the metal key. The half equation for the reduction reaction taking place at the cathode is shown below:
The positive electrode; the anode is usually made from the same metal you are plating onto the cathode. The metal anode will then slowly dissolve into the electrolyte and provide ions that will then be attracted to the cathode and plated onto it, electrodes such as this which take part in the cell reactions are called active electrodes. In copper plating as in the example discussed above a copper anode can be used. This copper anode will slowly dissolve into the copper sulfate electrolyte providing copper ions (Cu2+) that can then be plated onto cathode. Electroplating can also be carried out using inert electrodes, that is electrodes that take no part in the cell reactions as shown in the image opposite where the anode is made from a strip of inert platinum metal.
The ammeter is included in the circuit to monitor the size of the electrical current flowing.
If too large an electrical current is used the metal tends to plate very quickly onto the metal key and a poor coating is generally obtained, much better results are usually obtained if a small electrical current is used, the electroplating process will take longer to complete but a more even and long lasting metal plate is produced.
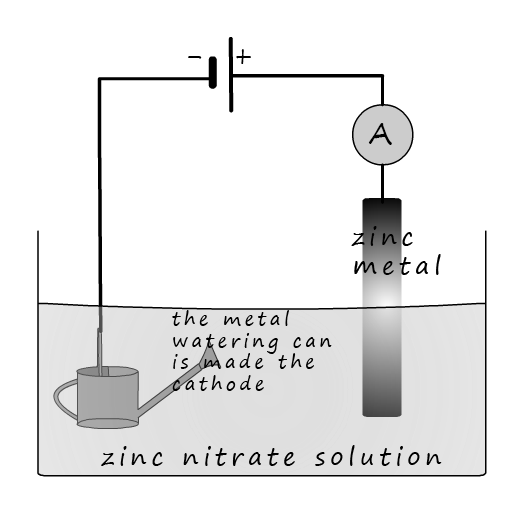
Galvanising is a common method used to prevent a metal object from corroding. Many cars are galvanised as an additional method used to prevent corrosion if the paint is damaged or chipped. Galvanising involves coating a metal, normally iron or steel with a thin layer of zinc. Zinc being more a more reactive metal will sacrifice itself to protect the iron or steel from corroding. Metal objects are galvanised by either dipping the object in a bath of molten zinc or by electroplating using a zinc solution; as shown in the image opposite. Here the steel watering can is given a thin plate of zinc by being electroplated. The watering can is made the cathode and when an electrical current flows the zinc ions in the solution will be attracted to the cathode and reduced:
If a strip of zinc is used at the anode then it will slowly dissolve away and replace the zinc ions which are reduced at the cathode:
This means that the overall reaction simply involves zinc from the anode dissolving to form zinc ions (Zn 2+) and these ions are then attracted to the cathode where they are reduced and plate onto the watering can.

Food cans are made from steel, however many foods are acidic or contain substances which can attack the steel can. Most food cans are designed to keep their contents "fresh" for several years and so they need to be constructed in a way that can resist the chemicals in food. The steel can could be electroplated with tin or even chromium. Tin and chromium are unreactive metals that will protect the steel can and prevent corrosion or oxidation of the metal. The can will also likely have some sort of plastic coating on the inside to help ensure no reaction occurs between the food and the can.