Higher and foundation tiers

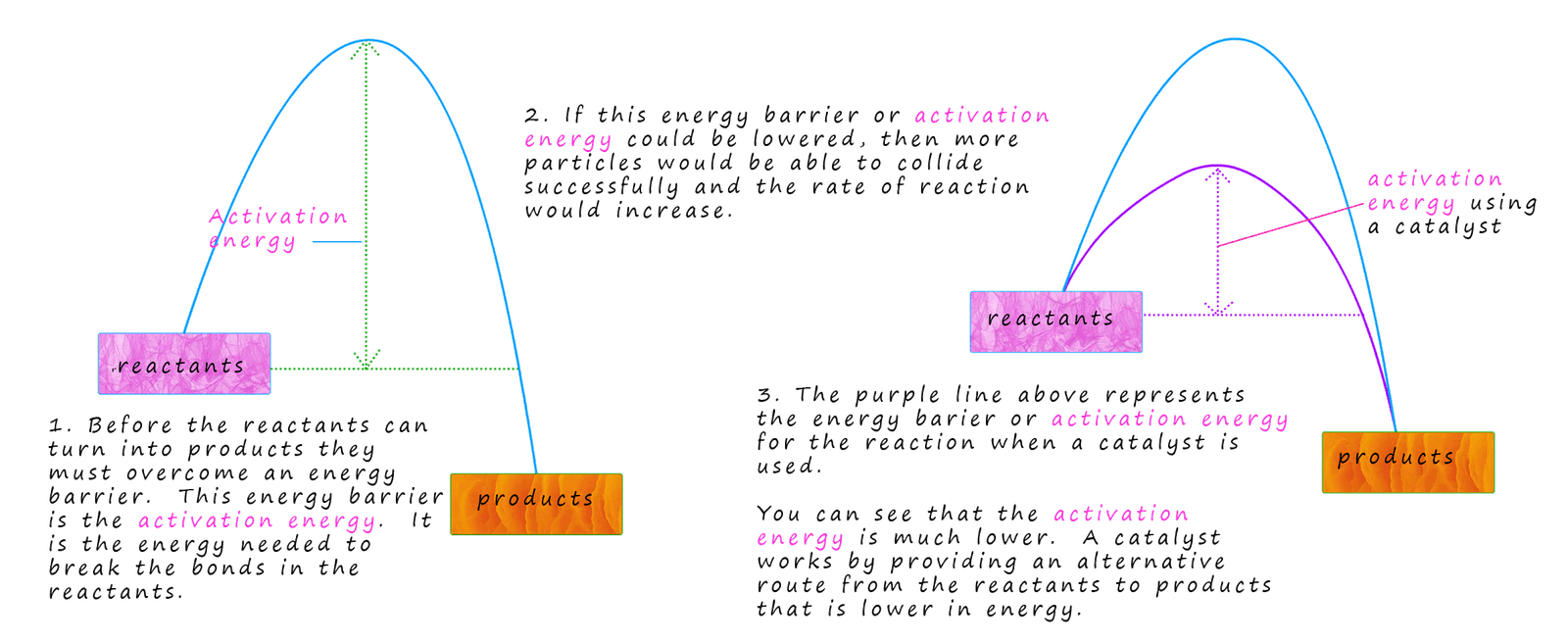
Catalysts are amazing substances! Catalysts are substances that speed up a chemical reaction without being used up. Catalysts are usually transition metals or transition metal compounds. As an example of a catalyst at work consider the following decomposition reaction of hydrogen peroxide:
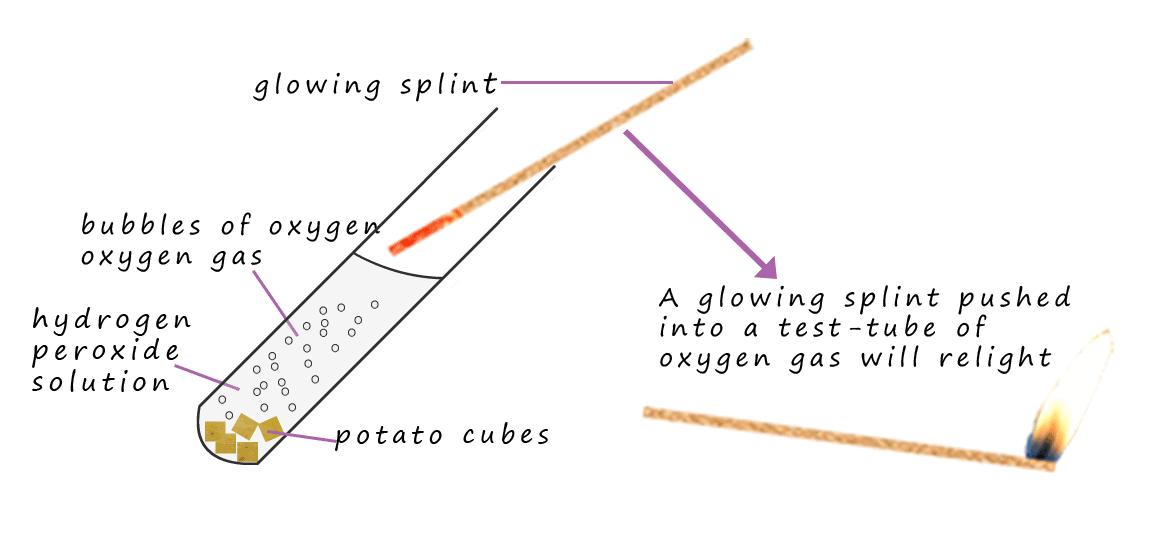
Now imagine for a minute that the school science lab technician has to prepare a class set of test-tubes full of oxygen gas for say a year 8 science lesson. How would they do it? Could the lab technician use the decomposition reaction of hydrogen peroxide to prepare the test-tubes of oxygen gas? Well in theory yes since hydrogen peroxide decomposes to release oxygen gas but not if the decomposition reaction is too slow; I am sure the year 8 class won't wait weeks or even years to get their test-tubes full of oxygen gas. Luckily this is where catalysts come into play. The lab technician set-up the apparatus below to collect the test tubes of oxygen gas.

You may notice that in the conical flask is a hydrogen peroxide solution and one spatulas of a solid compound called manganese dioxide has been added. Manganese dioxide
is a catalyst
for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. The hydrogen peroxide
will decompose violently and rapidly in the presence
of the manganese dioxide catalyst to form oxygen gas and water, so the lab tech will be able to collect a class set of test tubes all filled with oxygen gas in a few minutes thanks to catalysts.
Once the lab technician has filled a class set full of test-tubes for use by the students it would
be possible to
simply filter out the manganese dioxide catalyst since catalysts do NOT get used up in the reaction. It is also worth mentioning that since the
catalyst is not used up in the reaction only a small amount
of it is needed.
Many industrial and commercial processes use transition metal catalysts. These catalysts will speed up the chemical reactions and allow the factories to produce their products quicker. Catalysts can also reduce the temperature needed for a particular reaction to take place at and so reduce costs. Modern motor cars are also fitted catalytic converters in their exhaust systems, these catalytic converters reduce the emission of toxic gases from cars; examples of the use of catalysts include:

Enzymes are biological molecules that are used as catalysts in living organisms; they consist of large protein molecules. Enzymes are essential for many of the processes required to sustain life such as respiration and digestion. Enzymes in the human body are adapted to carry out a unique role; the table below lists a few examples of the many enzymes found in the human body and a brief explanation of the enzyme's role:
| Enzyme | Where is it produced? | What it does. |
|---|---|---|
| protease | stomach, pancreas and small intestine | Breaks down proteins into amino acids |
| lipase | pancreas and small intestine | Breaks down lipids (fats and oils) into fatty acids and glycerol. |
| carbohydrase (amylase) | salivary glands in the mouth and also in the pancreas and small intestine | Breaks down large carbohydrate molecules into smaller simpler sugar molecules. Amylase is an example of a carbohydrase enzyme that breaks down starch to form the simple sugar glucose. |

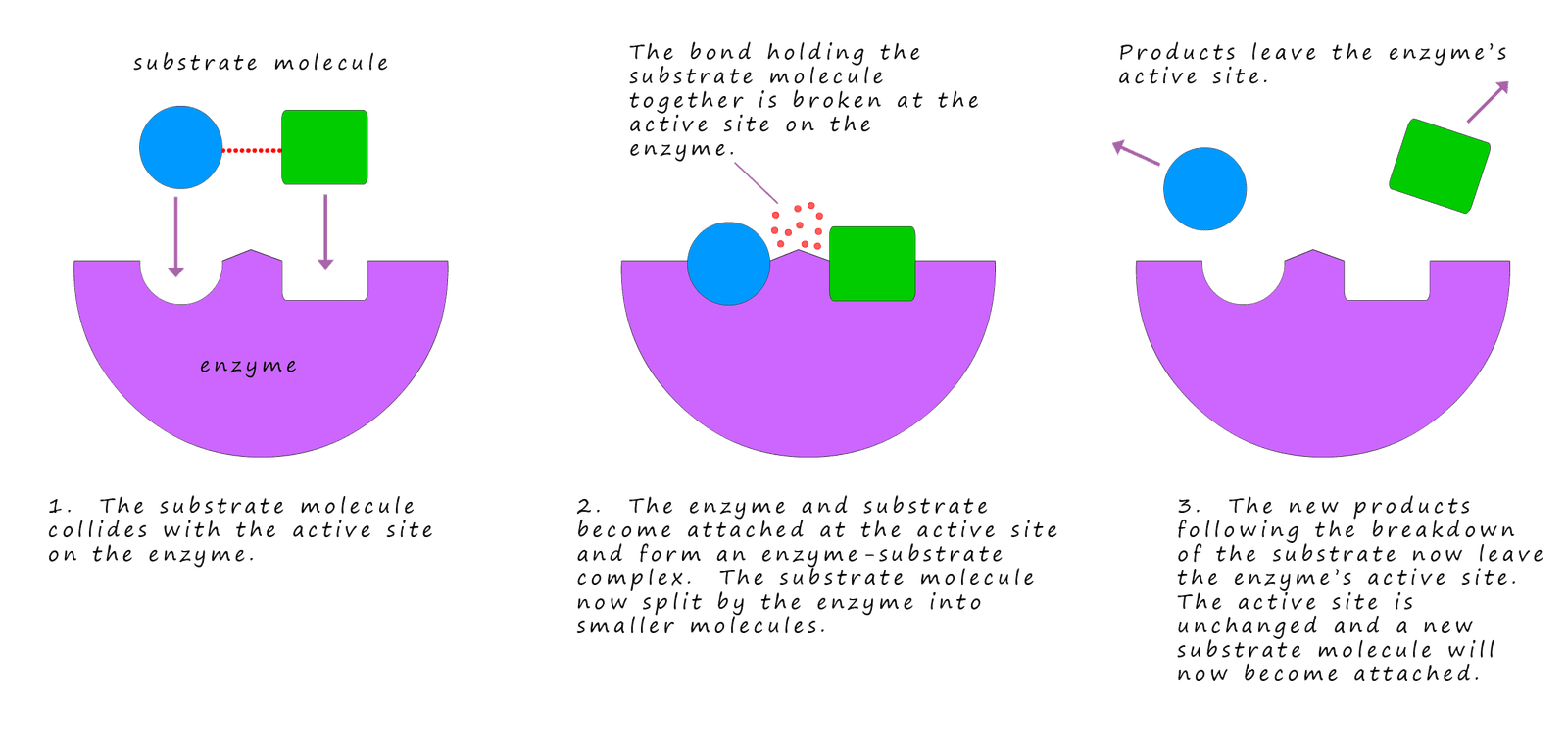
Enzymes are often referred to as biological catalysts. Enzymes are very large protein molecules which are made up of long chains of amino acids which are folded to give a very specific shape, the image opposite shows the structure of a typical enzyme. Each enzyme has its own specific shape and this specific shape is designed to allow only certain molecules (substrates) to fit into certain active sites within the enzyme's structure. These active sites are the business end of the enzyme and this is where the enzyme will perform its function or job. Some enzymes will break up large molecules into smaller one while others do the opposite and help assemble larger molecules from smaller one.
The image below shows a substrate molecule slotting into the active site in an enzyme. The enzyme and substrate fit together much like a lock and key; in fact the diagram below is often referred to as a lock and key diagram which is a good description since only one key will open a lock and only one substrate molecule will fit into the active site in the enzyme. Once the substrate slots into the active site they bind together to form an enzyme-substrate complex, a reaction will then take place very rapidly and the product will quickly leave the enzymes' active site. The active site on the enzyme is completely unchanged and as soon as the product is removed another substrate molecule will slot into the active site and the whole process will repeat again.
Biological washing powders and detergents often contain artificial enzymes which perform a similar job to those found in the human digestive system. This makes sense since the stains we are likely to get on our clothes may include food, sweat, grass and even blood if we are having a bad day. After lunch or dinner you may put your dirty dishes in a dishwasher and add a tablet which also contains enzymes to digest the food which remains on the plates and cutlery.
These washing powders and dishwasher tablets will contain enzymes that include proteases, lipases and carbohydrases to break up or digest the stains on our dirty clothes and the food remnants left on the dirty dishes in the dishwasher.