Higher and foundation tiers
The Greenhouse effect
 Without the natural greenhouse effect the
Earth would be too cold for life. Scientists estimate that the
Earth would be some 180C
colder without this natural warming effect. The small amount of
carbon dioxide and
other greenhouse gases such as methane and water vapour in the
atmosphere act like a blanket and trap enough of the sun's heat to keep the
temperature on our planet
within a stable range capable of maintaining life.
Without the natural greenhouse effect the
Earth would be too cold for life. Scientists estimate that the
Earth would be some 180C
colder without this natural warming effect. The small amount of
carbon dioxide and
other greenhouse gases such as methane and water vapour in the
atmosphere act like a blanket and trap enough of the sun's heat to keep the
temperature on our planet
within a stable range capable of maintaining life.
The swings in the Earth's temperature
and weather which we often complain about are very small and mild when compared to
the climates on other planets. Our climate and
temperature in the atmosphere are both
controlled by the presence of these greenhouse gases. If
the amounts of these gases increases then more of the Sun's heat will be trapped
in the atmosphere and temperatures
on Earth will start to rise. This
warming of the earth can lead to climate change, that is a long-term shift or change in the earth's average temperatures and weather patterns which can have a huge effect on all life on our planet.
Global warming
Over the last 150 years the amount of the greenhouse gas
carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
has increased by around 50% and many scientists are concerned that this is leading to a rise in global temperatures, this warming trend has been observed and documented over the past several decades and has led some scientists and environmentalists to declare a climate emergency. The rise in global temperatures is largely due to an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide gas in the atmosphere, this increase is mainly due to:
- The burning of fossil fuels such as coal and gas to generate
electricity as well as the burning of natural gas to
 heat our homes and to provide energy for many industries.
heat our homes and to provide energy for many industries.
- The burning of petrol and diesel as a fuel for transport in motor vehicles, trains etc.
- Widespread deforestation also releases large amounts of CO2
into the atmosphere and also prevents the removal
of CO2 by photosynthesis. The clearing of forests to make way for farming also has a large impact on the
amount of CO2 released since farming is an energy intensive activity.
Large areas of forest are being cleared in countries like Brazil and Indonesia to make way for cattle and to produce large amounts of timber to sell; this helps to boost their economies and provides jobs.
- Cows release either by burping or farting
up to 300 grams of the greenhouse gas methane per day and there are approximately
1.5 billion cows on Earth, this means that cows alone release around 142 million tonnes of
methane into the atmosphere every year and this amount is growing year upon year.
Methane is a much effective and potent than carbon dioxide gas at trapping
the Sun's heat in the atmosphere, although it has a shorter atmospheric lifespan than carbon dioxide, meaning its impact on climate change is less long-lasting. The increase in the food requirements of a
growing world population
means more farming
which ultimately means fewer forests and more cows. This cycle leads to an increase in both methane and carbon dioxide concentrations in
the atmosphere.

- In many parts of Asia rice is a major part of people's diet. The growing of rice in paddy fields also releases large amounts of
methane gas into the atmosphere. The paddy fields used to grow rice contain lots of slow
moving water with low oxygen levels, this water contain bacteria which produce large quantities of methane gas.
Greenhouse gases and climate change
Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and other gases such as methane
and water vapour are able to trap more of the Sun's
heat in the atmosphere; this has seen average global
temperatures rise. Many scientists believe that this increase
in global temperatures is one of the main drivers for
climate change which could cause:
- Melting of the polar ice-caps which will raise sea levels leading to widespread and catastrophic
flooding in many areas including countries such as Bangladesh, India, China, Philippines, Pakistan and Indonesia. Many of these countries have low lying coastlines or are located in areas where they experience intense rainfall leading to severe flooding.
- One consequence of the increase in the amounts of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is climate change; that is the change in the Earth's weather patterns and average global temperatures. In Britain we could see
more stormy wet winters and dry summers, with droughts and other extreme weather
patterns becoming much more common.

-
Many plants and animal species may die out and become extinct simply because they will be unable to adapt to their new environment
e.g. Beech trees are tall trees with fairly shallow roots and this shallow root system means they cannot tolerate
prolonged hot dry conditions such as those which are likely to be present in a world experiencing global warming.
- Some scientists believe that global warming may alter or change
hot water ocean currents that bring hot water
from the tropics to the cooler parts of the northern and southern hemispheres. If
these hot water currents stop or retreated further south then this could lead to significant climate changes, including potentially cooler temperatures in some regions e.g.
there is a warm water ocean current called the
Gulfstream which brings hot water from the Gulf of Mexico to warm the northern hemisphere, including Britain.
There
is evidence that the amount of hot water carried by the Gulfstream is reducing and it may even stop altogether. If this happened then the average temperatures which we in Britain experience would drop significantly.
- As carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere rise more of it will dissolve in the ocean. This will acidify the oceans and seas, resulting in a lower pH. This will harm many
aquatic plants and other organisms living in many marine environments. Rising sea
temperatures can also have dramatic effects on many marine
organisms e.g. rising sea temperatures can put enormous stresses on corals, living in coral reefs. The rising temperature stresses
the coral causing them to expel their algae. This results in coral bleaching where the coral loses their colour, this leaves the coral open to disease and may result in the coral dying.
How does the Greenhouse effect work?
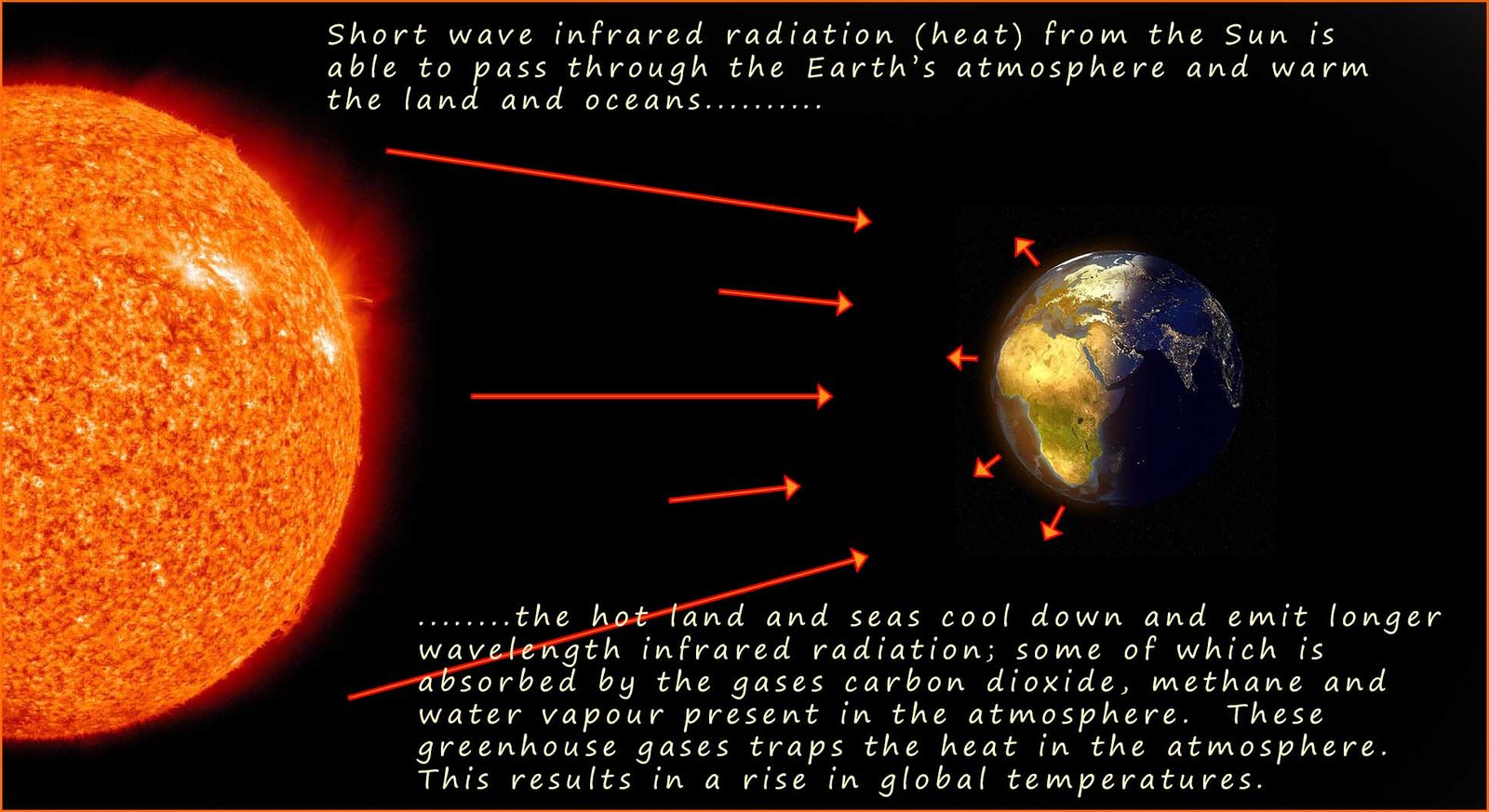
The Sun emits short wave infrared radiation
which provides the warm needed for life to thrive on Earth. This
short wave
infrared emitted by the Sun is able to pass through the
atmosphere and warm the land and oceans. When the hot land and sea
cool back down you might expect the infrared radiation (heat)
they give off to simply escape back into space, however the hot sea and land emits
infrared radiation of a longer wavelength
which certain gases such as carbon dioxide,
methane and water vapour are able to trap and
stop it from being emitted into space. The end result is that the heat
is trapped in the atmosphere - The Earth
warms
up; this is the Greenhouse effect. The image below summaries this:
Time to act?
 Since the industrial revolution
over 180 years ago the average global temperature has risen by about 1.10C. This might
not sound like much but many scientists are worried that if the average global temperature rises by 1.50C then many of the ecosystems
on Earth could become permanently damaged; there could be widespread climate change, this will likely result in
more severe flooding and droughts
across the globe with more severe and frequent storms/hurricanes/typhoons and the possibility of wide spread impacts on food
production and the ability of millions of people to access clean drinking water. Rapid climate change would also mean that many plants and animals
will not be able to adapt or change their behaviour to deal with this new climate
and will ultimately through loss of habitat and food become extinct.
Since the industrial revolution
over 180 years ago the average global temperature has risen by about 1.10C. This might
not sound like much but many scientists are worried that if the average global temperature rises by 1.50C then many of the ecosystems
on Earth could become permanently damaged; there could be widespread climate change, this will likely result in
more severe flooding and droughts
across the globe with more severe and frequent storms/hurricanes/typhoons and the possibility of wide spread impacts on food
production and the ability of millions of people to access clean drinking water. Rapid climate change would also mean that many plants and animals
will not be able to adapt or change their behaviour to deal with this new climate
and will ultimately through loss of habitat and food become extinct.
Many countries have signed agreements to cut their emissions
of carbon dioxide gas in order to try and prevent further warming. However not all countries have signed up to this
pledge, indeed some of the largest producers of greenhouse gases are reluctant to cut their emissions in case it damages
their economies following the havoc caused by the Covid-19 pandemic. Many countries are starting to invest in new green technologies which are less polluting in an attempt to reduce
the effects of climate change and to help them meet their emissions targets.
Fact or fiction
It is important to realize that not everyone agrees that the greenhouse effect is actually real; there is a small group of scientists and others who argue that the Earth has gone through natural periods in the past where average temperatures have risen and fallen over time. They would say that it is difficult for scientists to model such complex systems as the Earth's weather and climate, which leads to simplified models, opinions, and data that not everyone agrees with. As a scientist, you should consider all the facts available and not be swayed by the media or accepted opinion. Other people and organizations may have their own agendas, which could result in them twisting or distorting the facts. You need to consider all the information from all available sources before making up your own mind!
Key Points
- Human activities such as the burning of fossil fuels, agriculture, food production and many industrial processes are increasing
the amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases
are gases which trap
the infrared radiation (heat) from the sun and prevent it from escaping back into space.
Carbon dioxide, methane and water vapour
are all good greenhouse gases.
- Rising global temperatures due to the greenhouse effect can affect the weather patterns and climate of our planet.
- Rising global temperatures can result in:
- The ice caps present at the poles melting, this will result in sea levels rising and cause widespread global flooding.
- As the planet warms this will lead to weather patterns changing. Some areas will get more rain while others will become
drier. There is likely to be more storms, droughts, floods and heat waves. Plant and
animal species may become
extinct due to the fact they are unable to adapt and survive in fast changing habitats.
Practice questions
Next


 Without the natural greenhouse effect the
Earth would be too cold for life. Scientists estimate that the
Earth would be some 180C
colder without this natural warming effect. The small amount of
carbon dioxide and
other greenhouse gases such as methane and water vapour in the
atmosphere act like a blanket and trap enough of the sun's heat to keep the
temperature on our planet
within a stable range capable of maintaining life.
Without the natural greenhouse effect the
Earth would be too cold for life. Scientists estimate that the
Earth would be some 180C
colder without this natural warming effect. The small amount of
carbon dioxide and
other greenhouse gases such as methane and water vapour in the
atmosphere act like a blanket and trap enough of the sun's heat to keep the
temperature on our planet
within a stable range capable of maintaining life.  heat our homes and to provide energy for many industries.
heat our homes and to provide energy for many industries.


 Since the industrial revolution
over 180 years ago the average global temperature has risen by about 1.10C. This might
not sound like much but many scientists are worried that if the average global temperature rises by 1.50C then many of the ecosystems
on Earth could become permanently damaged; there could be widespread climate change, this will likely result in
more severe flooding and droughts
across the globe with more severe and frequent storms/hurricanes/typhoons and the possibility of wide spread impacts on food
production and the ability of millions of people to access clean drinking water. Rapid climate change would also mean that many plants and animals
will not be able to adapt or change their behaviour to deal with this new climate
and will ultimately through loss of habitat and food become extinct.
Since the industrial revolution
over 180 years ago the average global temperature has risen by about 1.10C. This might
not sound like much but many scientists are worried that if the average global temperature rises by 1.50C then many of the ecosystems
on Earth could become permanently damaged; there could be widespread climate change, this will likely result in
more severe flooding and droughts
across the globe with more severe and frequent storms/hurricanes/typhoons and the possibility of wide spread impacts on food
production and the ability of millions of people to access clean drinking water. Rapid climate change would also mean that many plants and animals
will not be able to adapt or change their behaviour to deal with this new climate
and will ultimately through loss of habitat and food become extinct.